Hard Fork (Blockchain)
Recently we came to know that Terra will be forked into two new chains. In this article we will discuss what is Hard fork and how forks work.
Forks in a Blockchain
Forks are changes in the functioning of a blockchain. A fork happens when a blockchain splits into two or more parallel paths forward.
These can occur in any crypto asset. When the network stakeholders, developers or community members disagree on the workings of the existing blockchain, alternative chains emerge known as Forks. These can be temporary or permanent ones.
Forks can also be intentional or unintentional. Accidental forks happen when few blocks are used at the same time. One chain ends up being longer than the other and the shorter chain is eventually abandoned. Intentional forks are done when rules are changed or altered for the good of crypto asset. As we have observed in the case of Terra, where the proposal is to do fork intentionally to safeguard LUNA from the de-pegging of UST.
Forks can be of two types – Hard Fork and Soft Fork
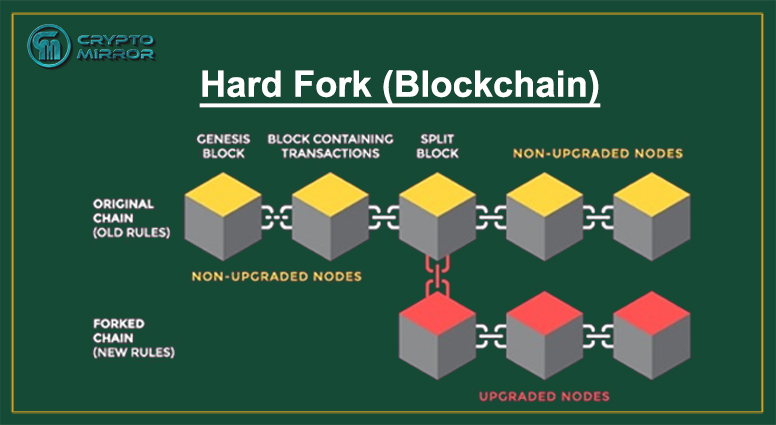
What is Hard Fork?
A Hard Fork means a drastic change with wide-range implications, in the protocol of the crypto asset’s blockchain. Protocols are basic set of rules through which data is shared between computers. A Hard Fork is implementing a new protocol that is incompatible with the existing one. This causes a split and the two networks run parallel then. Eventually the older one gets upgraded too.
There are blocks with old rules and then the blocks with the new rules. What may be invalid due to old rules may now be valid and all the nodes have to upgrade their software to work according to the new protocols. If the old protocol continues on with one chain working on the old protocol and another chain developed with the new protocol, this leads to a split.
Miners have to agree about the new protocols and what makes a block valid in the chain. Many digital currencies such as SegWot2x and Bitcoin Cash and so on have developed after this forking process.
Difference between Hard Fork and Soft Fork
Soft fork is a safer alternative to hard fork in which the upgraded nodes still see the older version as valid one. The older version still works compatibly in the soft fork after the changes are implemented. Basically, in a soft fork, small implementations, new features or functions are added that do not change the entire protocol of the blockchain. These changes are done on software level only. Whereas in hard fork, the entire protocol is changed.
Reasons for a Hard Fork
There can be a number of reasons why a blockchain underwent hard fork. Developers opt for hard fork for improving security loopholes or adding new functionalities.
Recently Ethereum created a hard fork to reverse the hack on DAO. This helped DAO token holders to get their Ether back. In this hard fork, the funds were relocated to a new smart contract where original owners can easily withdraw their funds.
Terraform Labs proposed a Hard fork of Terra into Terra Classic and Terra post algorithmic stable coin UST crash. Although the fork will be implemented after voting. There are reports that preliminary voters have rejected this proposal.